In this blog, following topics will be covered:
1. Classes & Objects
2. Constructors
3. Inheritance
4. Access Modifiers
5. Abstract
6. Virtual
7. Static
8. Sealed
9. Partial
1. Classes & Objects
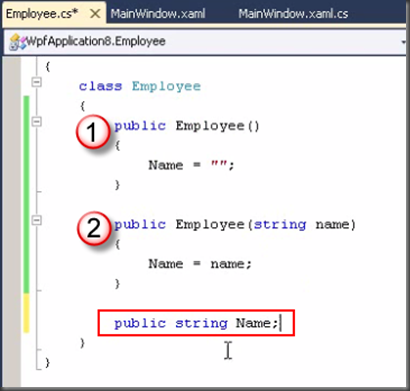
2. Constructors
1. No void
2. Method name are the same with class name
ctor + Tab to bring code snip of constructor
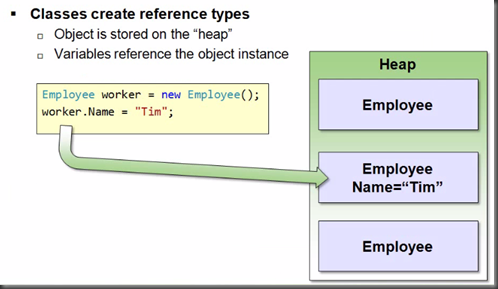
Reference Types
OO: Object Oriented Programming
3. Inheritance
Classes inherit from System.Object by default, for example, class Employee : Object by default
4. Access Modifiers
5. Abstract
1. Can’t use new() keywork to create an instance
2. If member is abstract, MUST implement it by override it
6. Virtual
1. The way to support Polymorphism
2. base.Method(), can be used to execute the virtual Method() in parent’s class
| Shape, Draw() | Circle, Draw() | Color |
| No Virtual | No Override | 1 Red, 100 Green |
| Virtual | No Override | 1 Red, 100 Green |
| Virtual | Override | 101 Red |
7. Static
1. Static member can only access by className.property => Calc._rand is allow
2. Static member can’t invoke the member through an object instance => a1._rand is not allow
3. Static member only has one copy of data, but instance field may has many (depends on how many instances has been created)
class Calc
{
public Calc(int rate)
{
_rate = rate;
}
public decimal GetResult()
{
return(_rate * _rand.NextDouble());
}
private int _rate;
static Random _rand = new Random();
}
Calc a1 = new Calc(5);
decimal result;
result = a1.GetResult();
8. Sealed
1. No one can inherit from a Sealed class
2. A lot of classes in .NET framework are Sealed class, System.String, for example
9. Partial
1. Span definitions in multiple files, and C# complier will merge them into one single class
2. LINQ to SQL & Entity Framework use a lot of partial methods















沒有留言:
張貼留言